Most surveys miss the mark. They either flood you with numbers that explain nothing or walls of text that no one has time to read. That’s what happens when you don’t know the difference between open-ended vs closed-ended questions.
- Closed-ended questions tell you what’s happening (fast, measurable, and clean).
- Open-ended questions reveal why it’s happening (giving you the real context behind the numbers).
The difference between a survey that collects noise and one that drives action lies in how well you combine the two. After analyzing hundreds of surveys and helping teams fix broken feedback loops, I’ve seen firsthand how the right mix can completely transform decision-making. Most people aren’t using these question types wrong; they’re just not using them intentionally.
In this guide, I’ll show you how to use open-ended vs closed-ended questions strategically, share examples of open-ended questions vs closed-ended questions, when to use each, how to connect them, and how to design surveys that lead to smarter, more actionable insights.
What Are Open-Ended Questions?

Open-ended questions hand the mic to your audience. Instead of boxing them into preset choices, you invite genuine answers in their own words, and often uncover insights a checklist would miss.
Purpose
Use open-ended questions for discovery, not confirmation. They reveal the reasons behind scores, behaviors, or decisions. When you’re unsure what to measure, these questions help you find it.
Examples
- “What is the biggest challenge you faced while using our product?”
- “What feature would you like us to add next?”
- “How could we make your experience better?”
Pros
- Context Over Counts: Capture stories, tone, and reasoning — not just numbers.
- Authentic Signal: Hear what truly matters to respondents.
- Discovery Value: Surface hidden pain points or new opportunities early.
Cons
- Time Heavy: Slower for both respondents and analysis.
- Messy to Organize: Responses need to be coded or categorized.
- Risk of Fatigue: Too many open fields can lead to short or empty replies.
Pro Tip: Automate the analysis. Modern survey tools can tag themes or detect sentiment automatically, letting you keep the depth of open-ended responses without getting buried in manual review.
What Are Closed-Ended Questions?
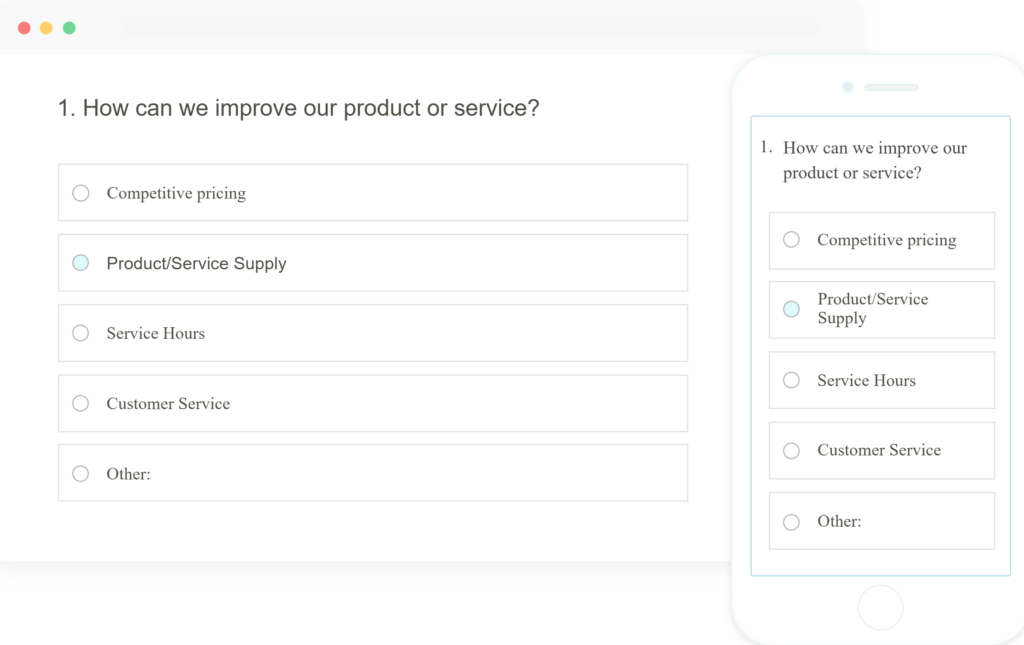
Closed-ended questions keep your data structured. Instead of asking people to explain, you offer defined choices and let them select. They’re quick, consistent, and easy to quantify: your survey’s high-speed data collectors.
Purpose
Use closed-ended questions when you already know what you’re measuring. They capture the underlying reasons behind opinions or behaviors, providing you with clean, comparable numbers that you can track over time.
Examples
- “How satisfied are you with our service?” (Scale of 1–5)
- “Would you recommend us to others?” (Yes or No)
- “How often do you use this feature?” (Daily, Weekly, Monthly, Rarely)
Pros
- Fast to Answer: Quick responses increase completion rates.
- Easy to Analyze: Structured data fits neatly into charts and dashboards.
- Reliable for Scale: Ideal for large samples that need statistical weight.
Cons
- Limited Depth: You get numbers, not explanations.
- Risk of Bias: Poorly worded options can steer answers.
- Few Surprises: You only measure what you thought to ask.
Closed-ended questions form the backbone of most surveys, from customer feedback to employee engagement. Use them to measure what matters, then follow with a single open-ended question to reveal why it matters.
Open-Ended vs Closed-Ended Questions
If open-ended questions are your microscope, closed-ended ones are your dashboard. One zooms in for context, the other zooms out for scale, and together they give you the full picture.
| Criteria | Open-Ended Questions | Closed-Ended Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Explore the “why” behind behaviors and opinions | Measure the “what” with structured, comparable data |
| Data Type | Qualitative (text-based) | Quantitative (numeric) |
| Pros | Contextual, revealing, and rich in detail | Fast, scalable, and simple to analyze |
| Cons | Time-consuming and harder to organize | Limited nuance, potential for bias |
| Best Used For | Discovery, feedback, and diagnostic insight | Tracking trends and validating hypotheses |
| Examples | “What made you choose our product?” | “Would you choose our product again?” |
| Pro Tip | Automate text or sentiment analysis to spot patterns faster | Keep response options balanced and neutral |
Use this table as a quick reference before drafting your next survey.
If you’re optimizing for speed and scale, lead with closed-ended questions. If you’re seeking depth and discovery, let open-ended questions take the mic.
Real-World Use Cases of Open-Ended vs Closed-Ended Questions
Let’s bring it down to ground level. Open- and closed-ended questions aren’t theory — they show up in real workflows every day. Here’s how different teams use them to make decisions faster and wiser:
- Customer Feedback & NPS: Use a rating scale to track satisfaction, then follow up with “What made you give that score?” The score shows sentiment; the comment explains what drives it. Here’s a quick Customer Feedback & NPS template you can try out:

- Product Research & Development: Ask “Which feature do you use most?” to measure adoption, then “What’s missing or hard to use?” to uncover unmet needs. Closed-ended data maps traction; open-ended input fuels innovation. Use this Product Research & Development template for ease:

- Employee Engagement: Combine “I feel recognized at work” with “What would make you feel more appreciated?” The first quantifies morale, the second reveals how to strengthen it. Don’t fret, here’s a quick Employee Engagement survey template for you:

- Customer Support & Service Quality: Ask “Was your issue resolved?” and “How could we have handled it better?” Together, they show both operational success and customer empathy. You can use this quick, in-context survey template for Customer Support & Service:
- Market & Brand Testing: Start with “Which concept or tagline do you prefer?” Then ask “Why that one?” The vote shows preference; the explanation reveals resonance.
- Education & Training: Track clarity with “How easy was this module to understand?” and follow with “What topic would you like explained differently?” You’ll capture both comprehension and improvement areas. Here’s a good Education & Training template for that:
Each of these pairs forms a simple insight loop: Numbers show what’s happening, stories explain why.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
How to Use Open-Ended vs Closed-Ended Questions in Surveys
By now, you know what open- and closed-ended questions can do. Using them effectively isn’t about templates, but more about designing a survey that feels like a thoughtful, two-way conversation. Here’s how:
1. Choose the Right Tool
Great surveys don’t just collect data; they shape the experience as it happens. Use a tool that connects questions logically, adapts to responses in real time, and delivers insights you can act on immediately.
For example, with tools like ProProfs Survey Maker, you can use AI survey maker to create surveys instantly and build branching flows, visualize both open and closed feedback together, and instantly see what matters most, no spreadsheet juggling required.
Choose a platform that feels like an assistant, not an admin. Here’s a video for you to learn how to create a survey effectively:
2. Begin With Intent, Not Curiosity
Every question should exist for a clear reason. If you can’t finish the sentence “I’m asking this because…”, cut it.
Open-ended questions explore the unknown; closed-ended ones validate what you already suspect. Plan your survey like a strategy session, not a brainstorm (purpose drives clarity).
3. Design the Experience, Not Just the Questions
A good survey keeps people engaged from start to finish. Mix short, structured questions with one or two open prompts for reflection. Keep a natural rhythm, not a checklist.
Structure it like this:
- Start with simple questions to warm people up.
- Add a few that invite reflection.
- End with a clean, easy finish.
Surveys are conversations in disguise. Design them like ones you’d actually want to have.
4. Automate the Heavy Lifting
Automation turns analysis from a chore into insight. Modern tools can tag themes, detect emotions, and surface patterns in seconds, leaving you to focus on what they mean, not how often they appear.
Use automation for scale; save manual review for nuance.
5. Treat Every Launch as a Pilot
There’s no such thing as a finished survey. Each round teaches you what works, what confuses people, and where engagement drops.
Trim friction, reword unclear items, and keep refining. The goal isn’t perfection but building a feedback process that keeps improving itself.
Open-Ended vs Closed-Ended Questions: Best Practices
Most teams treat open and closed questions like rival tools. They pick one, build the whole survey around it, and hope for the best. The real pros know better. You don’t choose between them, you choreograph them.
Many teams treat open and closed questions as if they compete with each other. In reality, the best surveys use both in harmony. You are not choosing between methods; you are learning how to combine them effectively.
1. Think in Layers, Not Types
Imagine your survey as a story. Closed-ended questions create the plot points that show what happened. Open-ended questions provide the dialogue that reveals how people felt about it. When placed in the right order, each type strengthens the meaning of the other.
You are not switching open-ended questions vs closed-ended questions research methods; you are shifting between overview and detail. Closed-ended data gives you scope, while open-ended feedback gives you depth.
2. Design the Flow Like a Conversation
Avoid adding an open-ended question after every multiple-choice item. Think conversationally instead. Ask, measure, and then listen.
A smooth flow often looks like this:
- Start with short, structured questions to warm people up.
- Add one or two open prompts where opinions are strongest.
- End with a single “Anything else?” question to capture ideas you did not think to ask.
This rhythm keeps people engaged and prevents data overload.
3. Use Data as a Trigger, Not a Trophy
Numbers are not the only goal. They show you where to explore further. When a score shifts or a pattern changes, open-ended feedback helps you understand why.
The strongest surveys do not stop at reporting. They create ongoing feedback loops that improve your understanding with every round.
4. Filter for Relevance, Not Curiosity
It is easy to overuse open-ended questions. They feel thorough but can add unnecessary noise. Each question should earn its place.
Ask yourself:
- Will this answer change what we do next?
- Is it essential or simply interesting?
If a question does not drive a decision, remove it. Skilled researchers know how to edit with focus.
5. Treat Feedback as a Loop, Not a Snapshot
Collecting data is not the end of the process. It is the beginning of the next cycle. Feed insights from open-ended answers into your next round of closed-ended questions. This continuous refinement helps your surveys become more predictive and useful over time.
The Core Trade-Off: Efficiency vs Depth
Every survey designer faces a key challenge. You want fast, measurable data, but you also want answers that reveal meaning and direction. The tension between these two goals is the core trade-off: efficiency versus depth.
Closed-Ended Questions: Fast and Scalable
Closed-ended questions act as your data engine. They collect quick, structured answers that are easy to compare and analyze across large groups.
If you need to track satisfaction across thousands of customers or monitor trends over time, this format is ideal. It provides speed, clarity, and measurable patterns.
Open-Ended Questions: Slower but More Insightful
Open-ended questions take longer for people to answer and for you to process, but they uncover motivations and frustrations that numbers alone cannot show.
For example, a customer who writes, “I rated it a 3 because support took too long,” gives you context behind the score. That single comment can explain an entire trend.
Finding the Right Balance
The most effective surveys mix both question types in sequence. Start with closed-ended questions to measure what is happening, then follow with open-ended prompts to understand why.
Think of it like building a map. Closed-ended questions draw the outline, and open-ended ones fill in the details. When used together, your survey stops reporting and starts explaining.
Biases and Methodological Risks in Open-Ended vs Closed-Ended Questions
Bias does not always appear obvious. It can slip into both the questions you write and the way you interpret the answers. The goal is not to eliminate it completely, which is impossible, but to identify and control it before it distorts your results.
Quick Overview of Common Biases:
| Question Type | Where Bias Appears | Examples | Impact on Data | How to Control It |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-Ended | In the options you provide | Suggestibility (wording influences responses), Acquiescence (people tend to agree), Social Desirability (people answer to look good) | Patterns may reflect your phrasing rather than true opinions | Test your survey before launch, keep wording neutral, watch for hesitation or skipped questions |
| Open-Ended | In how you interpret answers | Researcher Bias (seeing what you expect), Coding Drift (inconsistent categorization) | Themes may mirror assumptions instead of genuine feedback | Create a coding guide before analysis, have two reviewers tag responses, use AI tagging for speed but verify manually |
How to Minimize Bias Before and After Launch
Before you release your survey, test your questions with a small group. Look for signs of confusion, leading language, or emotional phrasing that might influence responses.
When analyzing results, separate what the data says from what you expect it to say. Having more than one reviewer or using automated tagging tools can help ensure objectivity and consistency.
Maintaining Reliability Over Time
Bias management is not a one-time task. Each new survey introduces small risks of drift in wording or interpretation. Review your design regularly, compare response patterns across versions, and document your coding rules to keep insights stable.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
Ask Smarter, Not More
Great surveys don’t happen by accident. They’re built by people who understand that asking the right mix of open and closed-ended questions is less about mechanics and more about mindset.
When you use them together, your surveys stop acting like forms and start behaving like conversations: the kind that reveal what your audience really thinks, not just what’s easy to measure.
So, design every question with purpose. Filter for what’s useful, automate what’s repetitive, and listen to what’s honest. Once you do that, your survey data stops being a report and starts becoming a roadmap. Or, best, you can use AI to create your surveys easily and effectively.
Ready to build a survey that actually listens? Start creating one today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s a smart ratio of open-ended to closed-ended questions?
There’s no fixed number, but a balanced survey usually includes one open-ended question for every five to seven closed-ended ones. That’s enough to capture depth without causing fatigue. The trick is to ask open-ended questions only where you truly need reasoning, not confirmation.
How can I encourage better answers to open-ended questions?
Make your prompts specific and purposeful. Instead of “Any feedback?”, try “What could make this process easier for you?” Specificity signals that you’ll actually use the answer, and respondents tend to put more thought into it.
How does AI help with open-ended responses?
AI doesn’t just summarize text. It also spots sentiment, intent, and patterns across hundreds of comments. That means you can detect rising issues or recurring praise even before someone categorizes them manually. It turns qualitative feedback into something you can act on faster.
What’s one common mistake teams make when combining both types of questions?
They overcollect. Too many open-ended questions feel exhausting; too many closed-ended ones feel robotic. The best surveys stay short but purposeful using open-ended questions only where they’ll change what you do next.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback!
 Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!






